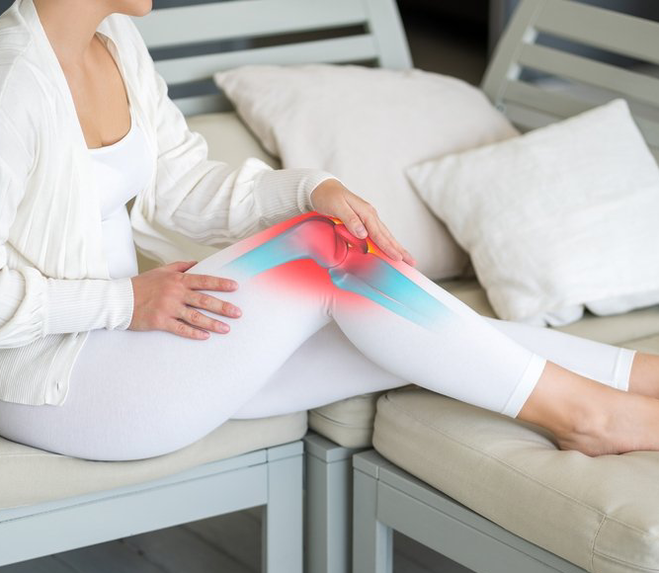
About the disease and possible complications
Types of Arthropathy
- The main variation is the result of a disruption of the relationship between the synthesis and degeneration processes of cartilage tissue, accompanied by dysfunction of chondrocytes (the main cells of cartilage).
- Secondary variants occur in previously modified joints when the normal relationship (conformity) of the joint surfaces is disrupted, and subsequently the load on the joint surfaces is redistributed and stress is concentrated in certain areas.
Symptoms of Arthropathy
- mechanical pain, caused by cartilage losing its shock-absorbing properties. Pain occurs with physical activity and is relieved with rest.
- Pain at night.Caused by stasis of venous blood and increased pressure of blood flowing within bones.
- The pain begins.It is short-lived and appears on getting up in the morning (the patient says he needs to be "dispelled"). These pains are caused by debris deposited on the cartilage plate; during movement, these debris are pushed into the joint and turn in, so the unpleasant sensation ceases.
- Meteor dependence.Pain may worsen when weather conditions change (increased air pressure, cold weather, high humidity).
- Lockdown pain.These are sudden painful sensations associated with the squeezing of pieces of bone or cartilage between the joint surfaces. Under the background of "blockade", the slightest movement of the joints stopped.
Course of Arthropathy During Pregnancy
Causes of joint arthritis
- "Excessive" weight increases the load on joints;
- wearing poor quality shoes;
- Concomitant diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Joint injuries.
Signs and Diagnosis of Arthropathy
- Radiography.In the early stages, X-ray symptoms of the disease mean little - these may be uneven narrowing of the joint space, slight compaction of the underlying bone, and small cysts in the area. In later stages, radiography can provide more information - the presence of marginal bone growth, changes in the shape of the joint surface, joint "mice" and areas of calcification in the joint capsule.
- Ultrasound examination of joints.Ultrasound scans are more informative for detecting the first symptoms of arthropathy. Signs such as intraarticular effusion, changes in cartilage plate thickness and structure, and secondary reactions in the joint capsule, tendon, and ligament compartments may be seen.
- Computed tomography or magnetic tomography.The diagnosis of joint arthritis is made in complex clinical cases, when a detailed assessment of the condition of the cartilage plates, subchondral areas of the bones and determination of the volume of synovial fluid, including the amount of synovial fluid, is required. Especially handstands.
Expert Opinion
Arthrodeforming arthropathy is one of the most common disorders of the musculoskeletal system, affecting 10-15% of the world's population. The insidious thing about this disease is that its progression is slow and gradual. At first, these are just short-term pains in a joint that people usually don't notice. Gradually, the severity of the pain syndrome becomes more severe, while the cyclical nature of the pain transforms into constant. Without treatment, the disease continues to progress with severe cartilage degeneration, which no longer responds to conservative treatment. To solve this problem, only a joint replacement is required - a complex and expensive procedure. Interventions to replace damaged joints with intact joints. -Proven implants. However, targeted medications and lifestyle changes can help significantly delay or avoid this surgery entirely. Therefore, if you develop joint pain, it is important to see your doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment of Arthropathy
Conservative treatment
- weight loss (if excessive);
- Carry out physical therapy to exclude prolonged periods of similar postures;
- Refusal to lift heavy objects or kneel for long periods of time (associated with some occupations).
Surgery
- joint puncture– For severe reactive synovitis. It not only removes inflammatory fluid, but also introduces corticosteroids to interrupt the pathological chain.
- Arthroscopic surgery, which involves introducing the instrument into the joint space through a small puncture and then visualizing it under magnification. These interventions can clean the joint and its inversion, flatten the cartilage plates, remove necrotic areas, "polish" the joint surface, etc.
- endoprosthesis– Considered a radical surgery, performed in cases of advanced pathological processes. Typically used for arthropathy of the knee or hip joints.